Table of Contents
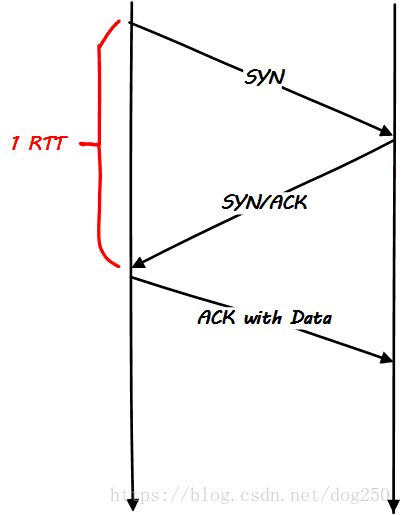
RTT(Round Trip Time)
| - | HTTP/2 OVER TLS1.2首次连接 | HTTP/2 OVER TLS1.2连接复用 | HTTP/2 OVER TLS1.3首次连接 | HTTP/2 OVER TLS1.3连接复用 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DNS解析 | 1-RTT | 0-RTT | 1-RTT | 0-RTT |
| TCP握手 | 1-RTT | 0-RTT | 1-RTT | 0-RTT |
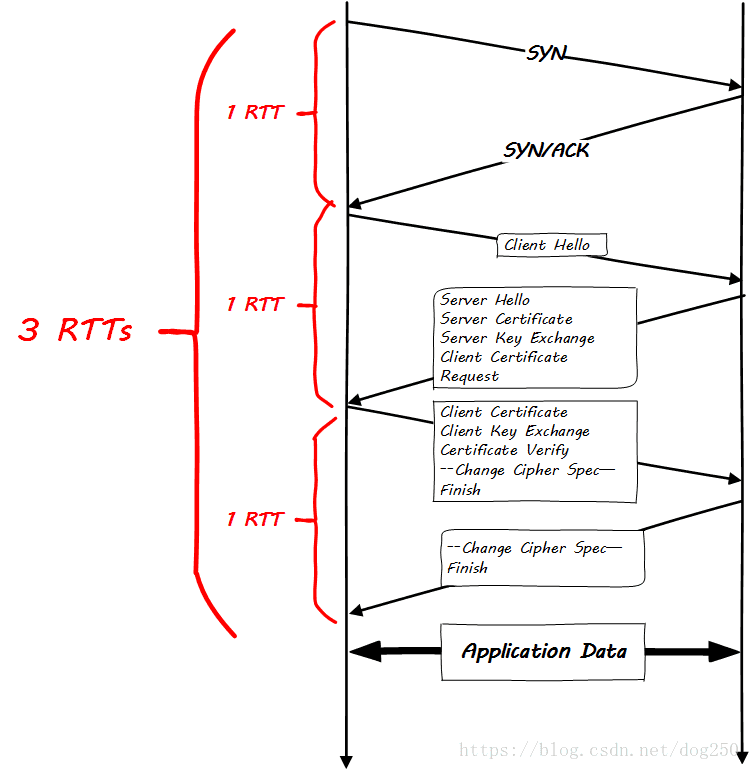
| TLS握手 | 2-RTT | 1-RTT | 1-RTT | 0-RTT |
| HTTP Request | 1-RTT | 1-RTT | 1-RTT | 1-RTT |
| 总计 | 5RTT | 2-RTT | 4-RTT | 1-RTT |
| - | QUIC 首次连接 | QUIC 连接复用 |
|---|---|---|
| QUIC握手 | 1-RTT | 0-RTT |
| HTTP Request | 1-RTT | 1-RTT |
| 总计 | 3-RTT | 1-RTT |
参考
QUIC
采用UDP传输层: QUIC 使用UDP(用户数据报协议)作为传输层协议,与传统的TCP相比,UDP减少了连接建立的延迟。TCP需要经历三次握手来建立连接,这会引入1个往返时间(1-RTT)的延迟。相比之下,QUIC的UDP传输层减少了这个握手过程,从而减少了建立连接的时间。这有助于提高网络通信的效率,尤其是对于那些对延迟要求较高的应用程序。
使用TLS 1.3协议: QUIC集成了TLS(传输层安全性)协议的最新版本,即TLS 1.3。TLS 1.3具有改进的安全性和性能特性,其中一个显著的特点是支持1-RTT和0-RTT握手。传统的TLS握手需要多个往返时间(RTT),而QUIC协议通过TLS 1.3允许客户端在TLS握手完成之前发送应用程序数据。这意味着在第一次握手时需要1-RTT,但之后,已建立连接的客户端可以使用缓存的信息来快速恢复TLS连接,只需0-1 RTT。这显著减少了建立连接的时间,使数据能够更快地传输,特别是对于重复连接的情况。
QUIC协议的基本功能包括:
独立的逻辑流: QUIC允许在单个连接上并行传输多个逻辑数据流。每个数据流都是独立管理的,这意味着一个数据流的延迟或中断不会影响其他数据流的传输。这有助于提高网络效率,特别是在处理多个请求和响应时。
一致的安全性: QUIC提供端到端的安全性,所有数据在传输过程中都经过加密。默认情况下,QUIC使用TLS 1.3来建立安全连接,确保数据的机密性和完整性。这有助于保护通信免受窃听和篡改。
低延迟: QUIC旨在减少网络通信的延迟。它采用快速的连接建立过程,减少了握手时间,并通过多路复用和快速重传等机制降低了数据传输的延迟。这对于实时应用程序和减少页面加载时间非常重要。
可靠性: QUIC提供可靠的数据传输,确保数据的完整性和准确性。它具有丢包恢复和重传机制,以应对网络中可能发生的数据包丢失或损坏情况。这有助于防止数据损坏和丢失。
避免HOL(Head-of-Line)阻塞: QUIC通过允许多个数据流在单个连接上独立传输,解决了HOL阻塞问题。这意味着即使一个数据流遇到问题,其他数据流仍然可以继续传输,而不会受到影响。这有助于提高整体效率和性能。
QUIC 协议的核心特性
0-RTT 连接建立
- 0-RTT 是 QUIC 协议中的一项关键功能,它旨在降低连接建立时的延迟。传统的 TCP 连接需要经过三次握手(SYN,SYN-ACK,ACK)才能建立连接,而每个往返时间(Round-Trip Time,RTT)都会增加延迟。在某些情况下,这可能导致不必要的等待时间。
- QUIC 的 0-RTT 特性允许客户端在连接初始化过程中同时发送数据,而无需等待握手完成。这是通过在第一次连接中包含加密后的应用程序数据实现的。这种方式使得在建立连接后立即发送数据成为可能,从而显著减少了初始请求的延迟。这对于移动应用、网页加载速度和实时通信非常重要,因为它可以加速用户体验。
无队头阻塞的多路复用
- 多路复用是 QUIC 的另一个核心特性,旨在解决传统 HTTP/1.1 和 HTTP/2 中存在的队头阻塞问题。在传统的 HTTP 中,如果某个请求的响应出现延迟或丢失,它将阻塞后续请求的处理,从而导致页面加载速度变慢。
- QUIC 允许多个逻辑数据流通过单个连接并行传输。每个数据流都有其独立的流量控制和优先级,这意味着一个数据流的延迟不会影响其他数据流。这提高了网络效率,允许快速响应多个请求,从而改善了用户体验。这对于现代网站、应用程序和多媒体流式传输非常重要。
无歧义重传
- 无歧义重传是 QUIC 的重要特性,用于确保数据的可靠传输。在不稳定的网络环境中,数据包可能会丢失或损坏,因此需要一种机制来恢复丢失的数据而不引入重复数据。
- QUIC 使用序列号来唯一标识数据包,并在接收方接收到数据包后发送确认。如果发送方没有收到确认,它会重新发送数据包,但只会重传丢失的数据包。这种机制确保了可靠的数据传输,而不会引入不必要的重传,从而提高了效率。
- 此外,QUIC 还支持拥塞控制,它可以根据网络条件调整数据包的发送速率,以避免网络拥塞。这有助于保持网络的稳定性和性能。
Connection ID
相较于TCP/IP使用五元组标识一条连接,QIUC在Connection层采用客户端随机产生的64位随机数作为Connection ID标识连接,这样IP或者端口发生变化时,只要ID 不变,这条连接依然维持,可以做到连接平滑迁移。
连接建立时使用UDP端口号来识别指定机器上的特定server,而一旦建立,连接通过其connection ID关联。
连接迁移
QUIC通过连接ID实现了连接迁移。
我们经常需要在WiFi和4G之间进行切换,比如我们在家里时使用WiFi,出门在路上,切换到4G或5G,到了商场,又连上了商场的WiFi,到了餐厅,又切换到了餐厅的WiFi,所以我们的日常生活中需要经常性的切换网络,那每一次的切换网络,都将导致我们的IP地址发生变化。
传统的TCP协议是以四元组(源IP地址、源端口号、目的ID地址、目的端口号)来标识一条连接,那么一旦四元组的任何一个元素发生了改变,这条连接就会断掉,那么这条连接中正在传输的数据就会断掉,切换到新的网络后可能需要重新去建立连接,然后重新发送数据。这将会导致用户的网络会“卡”一下。
但是,QUIC不再以四元组作为唯一标识,QUIC使用连接ID来标识一条连接,无论你的网络如何切换,只要连接ID不变,那么这条连接就不会断,这就叫连接迁移!
在一个keepalive周期内, Connection ID是不会变的, 比如60s, 也就是连接空闲60s就会生成新的Connection ID, 或者quic server重启, quic client重启
4元组,5元组,7元组
4元组即用4个维度来确定唯一连接,这4个维度分别是源Ip (source IP), 源端口(source port),目标Ip (destination IP), 目标端口(destination port)。
5元组是一个通信术语,英文名称为five-tuple,或5-tuple,通常指由源Ip (source IP), 源端口(source port),目标Ip (destination IP), 目标端口(destination port),4层通信协议 (the layer 4 protocol)等5个字段来表示一个会话,是会话哦。
7元组即用7个字段来确定网络流量,即源Ip (source IP), 源端口(source port),目标Ip (destination IP), 目标端口(destination port),4层通信协议 (the layer 4 protocol),服务类型(ToS byte),接口索引(Input logical interface (ifIndex))
openresty支持quic
add_header Alt-Svc 'quic=":443"; h3-27=":443";h3-25=":443"; h3-T050=":443"; h3-Q050=":443";h3-Q049=":443";h3-Q048=":443"; h3-Q046=":443"; h3-Q043=":443"'; # Advertise that QUIC is available
or
add_header Alt-Svc 'h3=":443"; ma=86400'; # Quic或HTTP/3响应头
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=63072000; includeSubdomains; preload"; # HSTS
HSTS 是 HTTP 严格传输安全(HTTP Strict Transport Security) 的缩写。 这是一种网站用来声明他们只能使用安全连接(HTTPS)访问的方法。
Alt-Svc 全称为“Alternative-Service”, 实际是在告诉客户端可以升级到备选服务(h3)协议上。这时再刷新页面,chrome会切换到h3协议上去。这样就实现了新旧协议的过渡升级。
HSTS 工作原理:
通常,当您在 Web 浏览器中输入 URL 时,您会跳过协议部分。 例如,你输入的是 www.acunetix.com,而不是 http://www.acunetix.com。 在这种情况下,浏览器假设你想使用 HTTP 协议,所以它在这个阶段发出一个 HTTP 请求 到 www.acunetix.com,同时,Web Server 会返回 301 状态码将请求重定向到 HTTPS 站点。 接下来浏览器使用 HTTPS 连接到 www.acunetix.com。 这时 HSTS 安全策略保护开始使用 HTTP 响应头:Strict-Transport-Security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload
响应头的 Strict-Transport-Security 给浏览器提供了详细的说明。 从现在开始,每个连接到该网站及其子域的下一年(31536000秒)从这个头被接收的时刻起必须是一个 HTTPS 连接。 HTTP 连接是完全不允许的。 如果浏览器接收到使用 HTTP 加载资源的请求,则必须尝试使用 HTTPS 请求替代。 如果 HTTPS 不可用,则必须直接终止连接。
server {
listen 443 ssl http2; # TCP listener for HTTP/2
listen 443 http3 reuseport; # UDP listener for QUIC+HTTP/3
ssl_protocols TLSv1.3; # QUIC requires TLS 1.3
ssl_certificate ssl/www.example.com.crt;
ssl_certificate_key ssl/www.example.com.key;
add_header Alt-Svc 'quic=":443"; h3-27=":443";h3-25=":443"; h3-T050=":443"; h3-Q050=":443";h3-Q049=":443";h3-Q048=":443"; h3-Q046=":443"; h3-Q043=":443"'; # Advertise that QUIC is available
}
server {
listen 443 ssl; # 启用 ssl
listen 443 quic; # 启用 HTTP/3
http2 on; # 启用 HTTP/2
add_header Alt-Svc 'h3=":443"; ma=86400'; # Quic或HTTP/3响应头
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=63072000; includeSubdomains; preload"; # HSTS
server_name www.jansora.com;
ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2 TLSv1.3; # 必须开启 TLSv1.3
ssl_certificate /etc/openresty/certs/jansora.com/www.jansora.com.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/openresty/certs/jansora.com/www.jansora.com.key;
location / {
proxy_pass_header Server;
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Scheme $scheme;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection upgrade;
proxy_pass http://192.168.36.100:3000;
}
}
nginx quic
docker run -d --name nginx-quic --restart always --network=host \
-v /usr/local/nginx-quic/conf/nginx.conf:/etc/nginx/nginx.conf:rw \
-v /usr/local/nginx-quic/conf.d:/etc/nginx/conf.d:rw \
-v /usr/local/nginx-quic/logs:/var/log/nginx:rw \
nginx:1.27-alpine3.19
/usr/local/nginx-quic/conf/nginx.conf
user nginx;
worker_processes auto;
worker_cpu_affinity auto;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log notice;
pid /var/run/nginx.pid;
events {
use epoll;
worker_connections 32767;
}
http {
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
}
/usr/local/nginx-quic/conf.d/http3.conf
server {
listen 8313 quic reuseport;
ssl_protocols TLSv1.3;
ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/conf.d/localhost.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/conf.d/localhost.key;
add_header Alt-Svc 'h3=":443"; ma=86400';
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=63072000; includeSubdomains; preload";
location / {
proxy_pass_header Server;
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Scheme $scheme;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection upgrade;
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:12346;
}
}
https://nginx.org/en/docs/quic.html
https://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_v3_module.html#http3_stream_buffer_size
openresty quic
docker run -d --name openresty-quic --restart always --network=host \
-v /usr/local/openresty-quic/conf/nginx.conf:/usr/local/openresty/nginx/conf/nginx.conf:rw \
-v /usr/local/openresty-quic/conf.d:/etc/nginx/conf.d:rw \
-v /usr/local/openresty-quic/logs:/var/log/nginx:rw \
openresty/openresty:1.25.3.1-alpine-fat
/usr/local/openresty-quic/conf/nginx.conf
# nginx.conf -- docker-openresty
#
# This file is installed to:
# `/usr/local/openresty/nginx/conf/nginx.conf`
# and is the file loaded by nginx at startup,
# unless the user specifies otherwise.
#
# It tracks the upstream OpenResty's `nginx.conf`, but removes the `server`
# section and adds this directive:
# `include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;`
#
# The `docker-openresty` file `nginx.vh.default.conf` is copied to
# `/etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf`. It contains the `server section
# of the upstream `nginx.conf`.
#
# See https://github.com/openresty/docker-openresty/blob/master/README.md#nginx-config-files
#
#user nobody;
#worker_processes 1;
worker_processes auto;
worker_cpu_affinity auto;
worker_shutdown_timeout 1h;
# Enables the use of JIT for regular expressions to speed-up their processing.
pcre_jit on;
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#pid logs/nginx.pid;
events {
use epoll;
worker_connections 32767;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
# Enables or disables the use of underscores in client request header fields.
# When the use of underscores is disabled, request header fields whose names contain underscores are marked as invalid and become subject to the ignore_invalid_headers directive.
# underscores_in_headers off;
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#access_log logs/access.log main;
# Log in JSON Format
# log_format nginxlog_json escape=json '{ "timestamp": "$time_iso8601", '
# '"remote_addr": "$remote_addr", '
# '"body_bytes_sent": $body_bytes_sent, '
# '"request_time": $request_time, '
# '"response_status": $status, '
# '"request": "$request", '
# '"request_method": "$request_method", '
# '"host": "$host",'
# '"upstream_addr": "$upstream_addr",'
# '"http_x_forwarded_for": "$http_x_forwarded_for",'
# '"http_referrer": "$http_referer", '
# '"http_user_agent": "$http_user_agent", '
# '"http_version": "$server_protocol", '
# '"nginx_access": true }';
# access_log /dev/stdout nginxlog_json;
# See Move default writable paths to a dedicated directory (#119)
# https://github.com/openresty/docker-openresty/issues/119
client_body_temp_path /var/run/openresty/nginx-client-body;
proxy_temp_path /var/run/openresty/nginx-proxy;
fastcgi_temp_path /var/run/openresty/nginx-fastcgi;
uwsgi_temp_path /var/run/openresty/nginx-uwsgi;
scgi_temp_path /var/run/openresty/nginx-scgi;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
# Don't reveal OpenResty version to clients.
# server_tokens off;
}
/usr/local/openresty-quic/conf.d/http3.conf
server {
listen 8312 quic reuseport;
ssl_protocols TLSv1.3;
http3 on;
http3_stream_buffer_size 10240k;
ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/conf.d/localhost.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/conf.d/localhost.key;
add_header Alt-Svc 'h3=":443"; ma=86400';
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=63072000; includeSubdomains; preload";
location / {
proxy_pass_header Server;
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Scheme $scheme;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection upgrade;
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:12346;
}
}
go-quic
https://nginx.org/en/docs/quic.html
https://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_v3_module.html#http3_stream_buffer_size
设置一下缓冲区大小 对应nginx的http3_stream_buffer_size
failed to sufficiently increase receive buffer size (was: 208 kiB, wanted: 7168 kiB, got: 416 kiB). See https://github.com/quic-go/quic-go/wiki/UDP-Buffer-Sizes for details.
linux socket 缓存:
默认的 Linux buffer size 的最大值是非常小的,tcp 的内存是基于系统的内存自动计算的,你能通过键入以下命令找到实际的值:
$ cat /proc/sys/net/ipv4/tcp_mem
默认的和最大的接收数据包内存大小:
$ cat /proc/sys/net/core/rmem_default
$ cat /proc/sys/net/core/rmem_max
默认的和最大的发送数据包内存的大小:
$ cat /proc/sys/net/core/wmem_default
$ cat /proc/sys/net/core/wmem_max
最大的内存 buffers 的选项:
$ cat /proc/sys/net/core/optmem_max
sysctl -w net.core.rmem_max=7500000
sysctl -w net.core.wmem_max=7500000
docker run -itd \
--restart=always \
--name=quic \
--sysctl net.core.rmem_max=10240000 --sysctl net.core.wmem_max=10240000 \
--network=host \
-e env=pro \
-v /usr/local/pcdn/quic/config:/app/manifest/config/:rw \
quic:v1.0
curl
curl --http3 https://nghttp2.org:8443/
检查浏览器是否支持http3协议:https://http3.is https://http3check.net/?host=http3check.net
Use only HTTP/3:
curl --http3-only https://example.org:4433/
Use HTTP/3 with fallback to HTTP/2 or HTTP/1.1 (see "HTTPS eyeballing" below):
curl --http3 https://example.org:4433/
Upgrade via Alt-Svc:
curl --alt-svc altsvc.cache https://curl.se/
自己编译
使用 QuicTLS 编译 Nginx 并开启 Quic 或 HTTP/3
cd wget https://github.com/quictls/openssl/archive/refs/tags/openssl-3.1.5-quic1.tar.gz && \
tar -xzf openssl-3.1.5-quic1.tar.gz && \
cd openssl-openssl-3.1.5-quic1 && \
./config --prefix=/usr/local/openresty/quictls/build no-shared && \
make && \
make install_sw
--with-openssl 是源码路径
--with-stream \
--with-stream_ssl_module \
--with-http_v3_module \
--with-http_ssl_module \
--with-openssl='../openssl-openssl-3.1.5-quic1' \
--with-cc-opt='-I/usr/local/openresty/quictls/build/include' \
--with-ld-opt='-L/usr/local/openresty/quictls/build/lib'
http/3 client
java
https://bitbucket.org/pjtr/flupke
https://github.com/ptrd/flupke
https://jetty.org/docs/jetty/11/programming-guide/client/http.html#transport-http3
golang
quic-go
python
https://github.com/aiortc/aioquic
dart
https://pub.dev/packages/http
https://pub.dev/packages/cronet_http
Cronet
既然我们知道 HTTP/3 和 QUIC 可以得到更好的体验,那就不得不说 Cronet,因为 Cronet 是 Chromium 网络堆栈,所以才被称为 Cronet ,它和 Chromium 使用相同的网络引擎。
而 Cronet 核心网络引擎完全基于C/C++,所以它除了可以在 Android 中使用之外,也可以通过 FFI 的方式被 Dart 使用
术语
HTTP-over-QUIC
HTTP/3 在2018年前叫HTTP-over-QUIC
2018年 IETF(Internet Engineering Task Force,定义互联网协议的标准机构)提议将HTTP-over-QUIC 更名为HTTP/3
RTT
往返时间(Round-Trip Time,RTT)是一个网络性能指标,用于衡量数据包从发送端到接收端再返回发送端所需的时间。
一些相关规范草案:
0-RTT
H3-29
H3-27
H3-Q050
H3-T051
H3-T050
H3-Q046
H3-Q043
Q046
Q043